Body Mass Index (BMI) is the measurement of choice for many health care practitioners and researchers studying obesity. BMI uses a mathematical formula that takes into account both a person’s weight and height (the formula is your weight in kilograms divided by your height in meters squared).
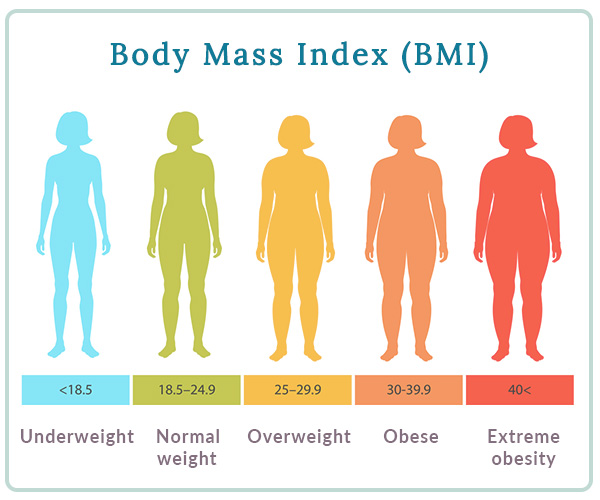
You can find your BMI on the chart below using your height in feet and inches and your weight in pounds.
Bear in mind that while the BMI chart can give you a rough idea of whether you’re at your optimal weight, the BMI formula does not factor your total body fat, muscle, or and water into the overall health equation. This is addressed more holistically by bioimpedence analysis models.
Some researchers observe that the waist-to-hip ratio is a more accurate means than the BMI for determining cardiovascular disease risk. Waist-to-hip ratio is easily calculated by dividing your waist measurement by your hip measurement. The cut-off limit for risk is <0.85 for women, and <0.90 and below for men. A ratio higher than these figures indicates a greater risk for cardiovascular disease.
Yusuf, S., et al. 2005. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: A case-control study. The Lancet, 366 (9497), 1640–1649.